Run the MEGAHIT assembler¶
MEGAHIT is a very fast, quite good assembler designed for metagenomes.
First, install it:
cd
git clone https://github.com/voutcn/megahit.git
cd megahit
make
Now, download some data:
cd /mnt/data
curl -O https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/dib-training.ucdavis.edu/metagenomics-scripps-2016-10-12/SRR1976948.abundtrim.subset.pe.fq.gz
curl -O https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/dib-training.ucdavis.edu/metagenomics-scripps-2016-10-12/SRR1977249.abundtrim.subset.pe.fq.gz
These are data that have been run through k-mer abundance trimming (see K-mer Spectral Error Trimming) and subsampled so that we can run an assembly in a fairly short time period :).
Now, finally, run the assembler!
mkdir /mnt/assembly
cd /mnt/assembly
ln -fs ../data/*.subset.pe.fq.gz .
~/megahit/megahit --12 SRR1976948.abundtrim.subset.pe.fq.gz,SRR1977249.abundtrim.subset.pe.fq.gz \
-o combined
This will take about 25 minutes; at the end you should see output like this:
... 12787984 bp, min 200 bp, max 61353 bp, avg 1377 bp, N50 3367 bp
... ALL DONE. Time elapsed: 1592.503825 seconds
The output assembly will be in combined/final.contigs.fa.
While the assembly runs...¶
How assembly works - whiteboarding the De Bruijn graph approach.
Interpreting the MEGAHIT working output :)
What does, and doesn’t, assemble?
How good is assembly anyway?
Discussion:
Why would we assemble, vs looking at raw reads? What are the advantages and disadvantages?
What are the technology tradeoffs between Illumina HiSeq, Illumina MiSeq, and PacBio? (Also see this paper.)
What kind of experimental design considerations should you have if you plan to assemble?
Some figures: the first two come from work by Dr. Sherine Awad on analyzing the data from Shakya et al (2014). The third comes from an analysis of read search vs contig search of a protein database.
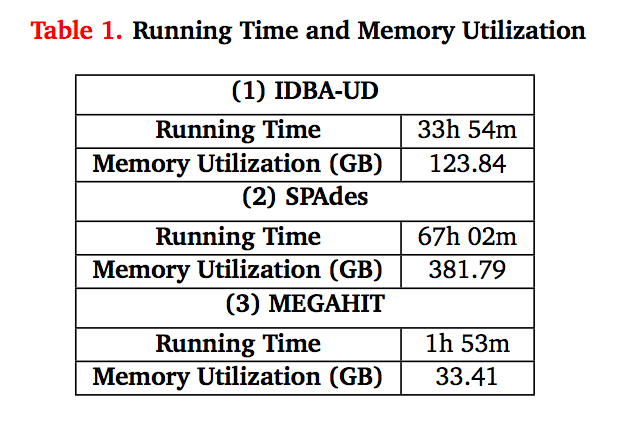
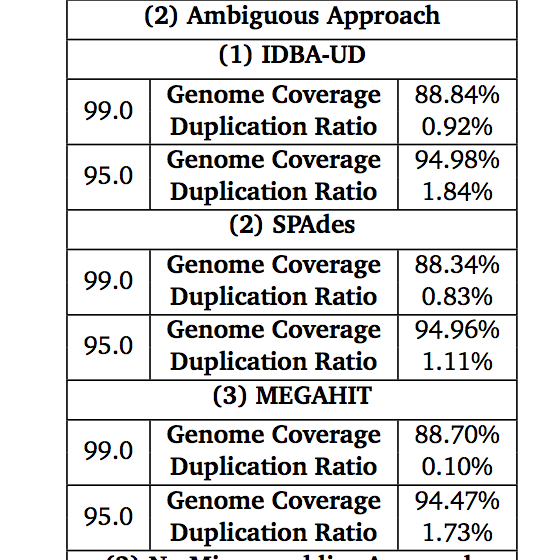
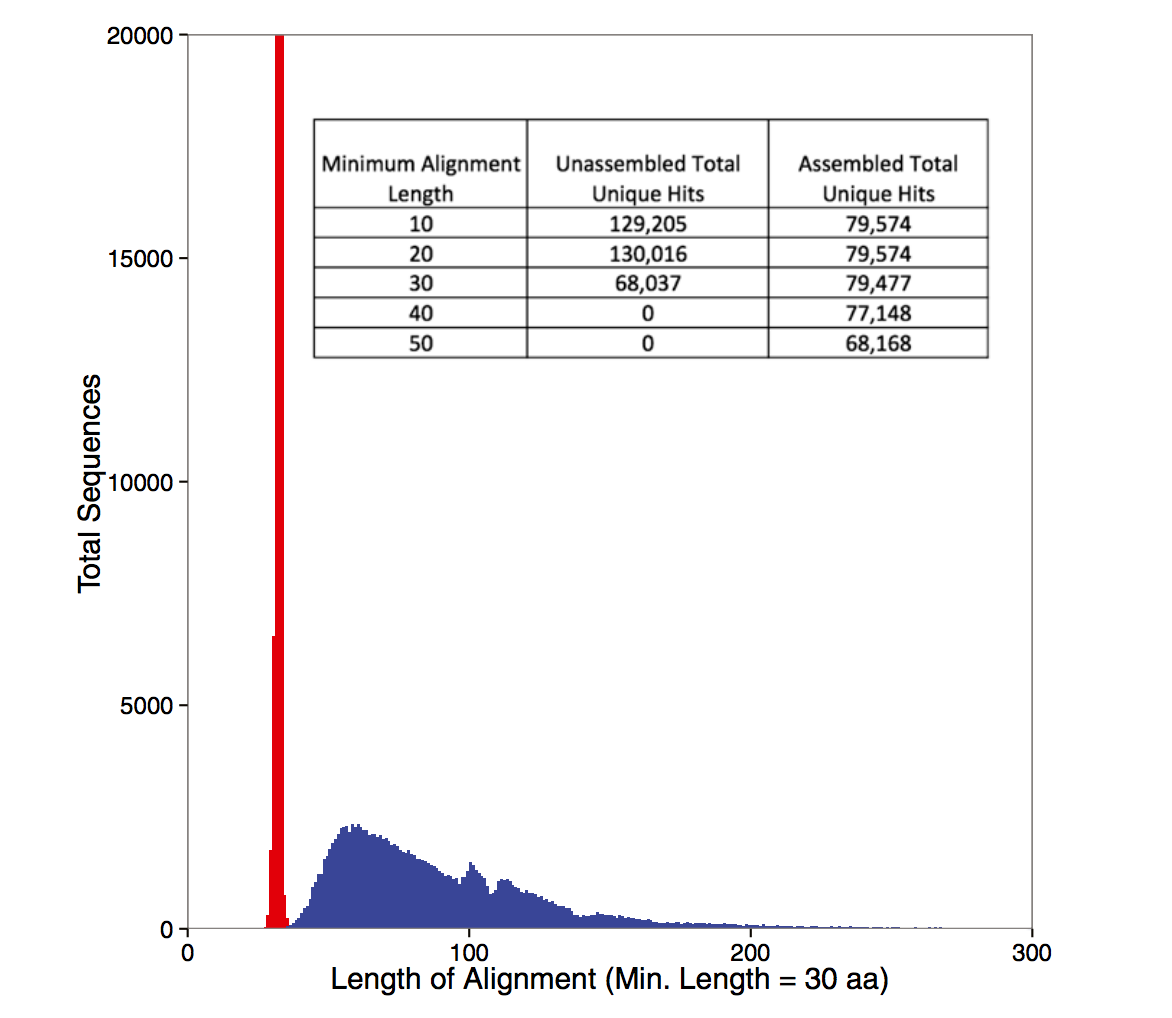
After the assembly is finished¶
At this point we can do a bunch of things:
- annotate the assembly (Annotation with Prokka);
- evaluate the assembly’s inclusion of k-mers and reads;
- set up a BLAST database so that we can search it for genes of interest;
- quantify the abundance of the contigs or genes in the assembly, using the original read data set (Gene Abundance Estimation with Salmon);
- bin the contigs in the assembly into species bins;
LICENSE: This documentation and all textual/graphic site content is licensed under the Creative Commons - 0 License (CC0) -- fork @ github. Presentations (PPT/PDF) and PDFs are the property of their respective owners and are under the terms indicated within the presentation.